Heron's formula
Heron's formula (sometimes called Hero's formula), named after Hero of Alexandria, gives the area of a triangle by requiring no arbitrary choice of side as base or vertex as origin, contrary to other formulas for the area of a triangle, such as half the base times the height or half the norm of a cross product of two sides.
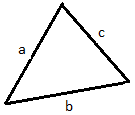
Formulae used
a = side-a of triangle
b = side-b of triangle
c = side-c of triangle
p = (a + b + c)/2
Area of triangle = √(p × (p-a) × (p-b) × (p-c))
Perimeter of triangle = a + b + c